My 1-Day SEO Strategy
How to Optimize your SEO in JUST 8 HOURS
01
Some agencies love to take weeks to define a strategy. But what if I told you that you just need ONE DAY to do that? There’s a condition, though.
02
Building an SEO strategy in a day is about being organized and focusing on the most impactful tasks. Plus, it’s all about taking action. So… let’s start NOW 
03
MORNING  Keyword Research & Competitor Analysis.
Keyword Research & Competitor Analysis.
04
Keyword Research & Competitor Analysis: Start by identifying the keywords your target audience is searching for. Use tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Google Keyword Planner to find high-traffic, low-competition keywords. Then, analyze your top competitors to understand their keyword strategy and find gaps you can exploit.
05
ACTION  : Make a list of 20–30 relevant keywords to target.
: Make a list of 20–30 relevant keywords to target.
06
MID-MORNING  Technical SEO Audit
Technical SEO Audit
07
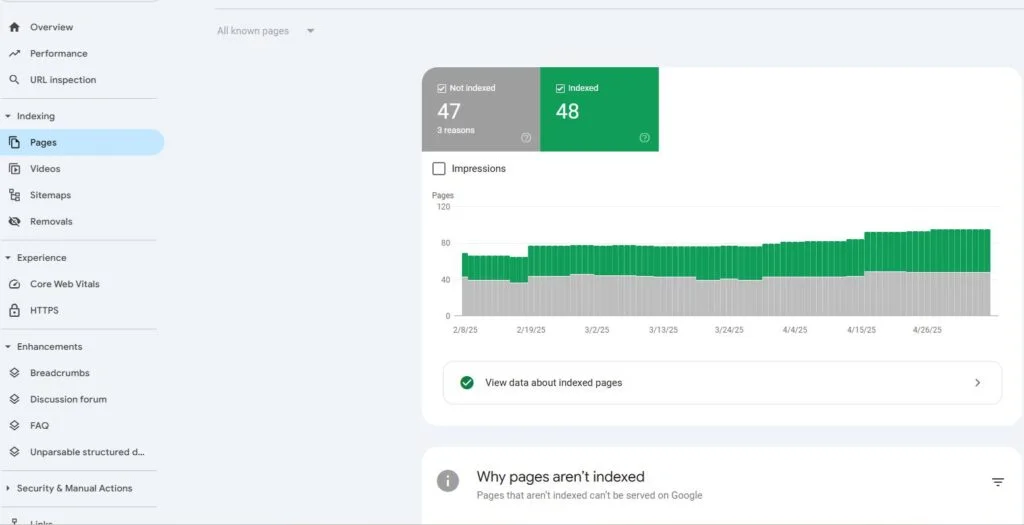
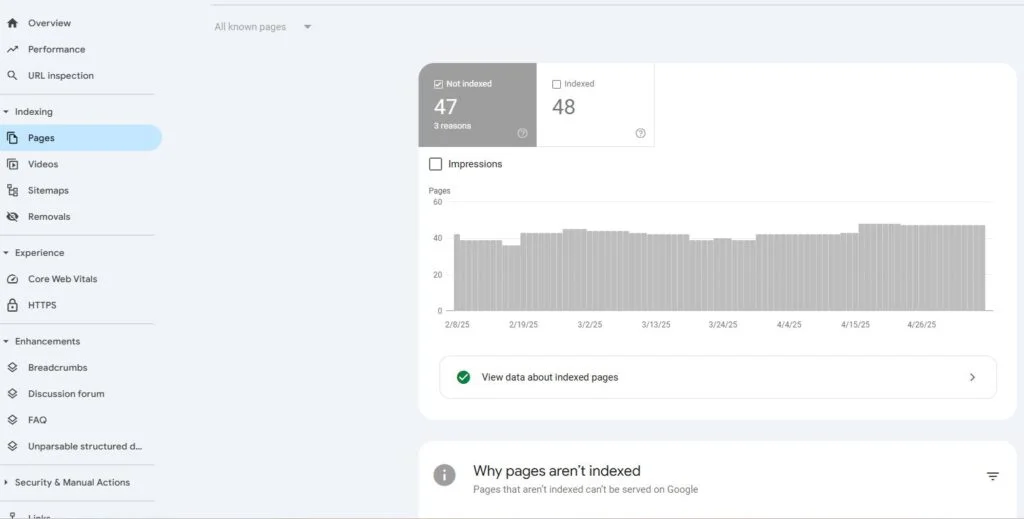
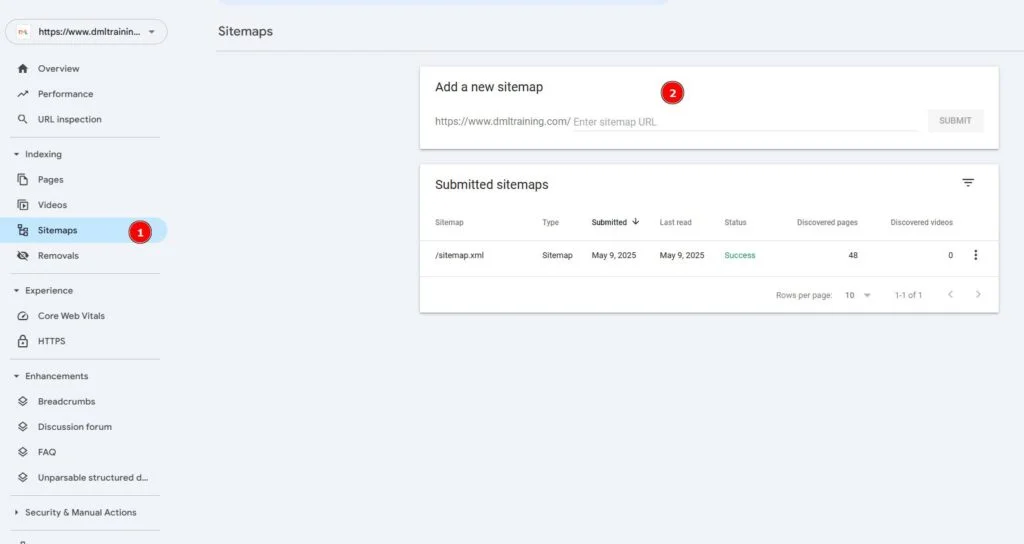
Technical SEO Audit  Use tools like Screaming Frog or Google Search Console to perform a quick audit of your website. Look for issues like broken links, slow loading times, or missing meta tags (title & description). Fix these issues to make sure that search engines can easily crawl and index your site.
Use tools like Screaming Frog or Google Search Console to perform a quick audit of your website. Look for issues like broken links, slow loading times, or missing meta tags (title & description). Fix these issues to make sure that search engines can easily crawl and index your site.
08
ACTION  Fix 3–5 technical SEO issues identified in the audit.
Fix 3–5 technical SEO issues identified in the audit.
09
LUNCHTIME  SEO Content Strategy
SEO Content Strategy
10
SEO Content Strategy  Plan out your content based on the keywords you identified. Decide on the types of content you will create (blogs, videos, infographics) and map out a content calendar. Make sure your content is aligned with the needs and interests of your audience.
Plan out your content based on the keywords you identified. Decide on the types of content you will create (blogs, videos, infographics) and map out a content calendar. Make sure your content is aligned with the needs and interests of your audience.
11
ACTION  Outline 3-4 content pieces around your main keywords.
Outline 3-4 content pieces around your main keywords.
12
AFTERNOON  On-Page Optimisation
On-Page Optimisation
13
On-Page Optimization  Focus on optimizing the key elements of your web pages. Don’t spread yourself too thin. This includes title tags, meta descriptions, headers (H1, H2, etc.), images, and internal linking. Make sure each page is optimized for the specific keyword you’re targeting + use secondary keywords.
Focus on optimizing the key elements of your web pages. Don’t spread yourself too thin. This includes title tags, meta descriptions, headers (H1, H2, etc.), images, and internal linking. Make sure each page is optimized for the specific keyword you’re targeting + use secondary keywords.
14
ACTION  Optimize the top 5 most important pages on your site.
Optimize the top 5 most important pages on your site.
15
LATE AFTERNOON  Backlink Strategy
Backlink Strategy
16
Define a Backlink Strategy  Identify easy backlink opportunities, such as reclaiming unlinked brand mentions or submitting your site to relevant directories. Reach out to existing partners or use press releases or HARO (Help a Reporter Out) to gain high-quality backlinks.
Identify easy backlink opportunities, such as reclaiming unlinked brand mentions or submitting your site to relevant directories. Reach out to existing partners or use press releases or HARO (Help a Reporter Out) to gain high-quality backlinks.
17
ACTION  Reach out to 5 sites for backlink opportunities.
Reach out to 5 sites for backlink opportunities.
18
EARLY EVENING  Local SEO and Social Media.
Local SEO and Social Media.
19
Local SEO and Social Media  If you have a local business, optimize your Google My Business listing and get listed in local directories. Use social media to share your content and build a community. SEO-wise, engaging with your audience on social platforms can drive traffic and backlinks.
If you have a local business, optimize your Google My Business listing and get listed in local directories. Use social media to share your content and build a community. SEO-wise, engaging with your audience on social platforms can drive traffic and backlinks.
20
ACTION  Optimize your Google My Business profile and schedule 3 social media posts.
Optimize your Google My Business profile and schedule 3 social media posts.
21
EVENING  Review and Set KPIs
Review and Set KPIs
22
Review and Set KPIs  Wrap up your day by reviewing the work you’ve done. Set clear KPIs to measure the success of your strategy.
Wrap up your day by reviewing the work you’ve done. Set clear KPIs to measure the success of your strategy.
23
ACTION  Set 3-5 KPIs to track over the next month.
Set 3-5 KPIs to track over the next month.
My advice?
Just do your best! Define the best strategy for your website, but don’t try to tick all boxes.
 : A fun nod to Ahrefs’ own search engine!
: A fun nod to Ahrefs’ own search engine!






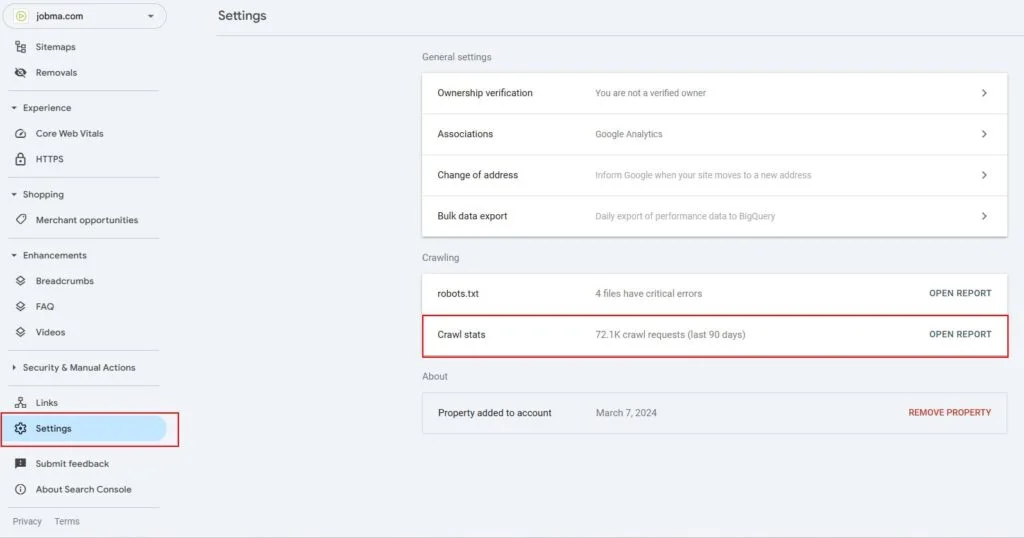
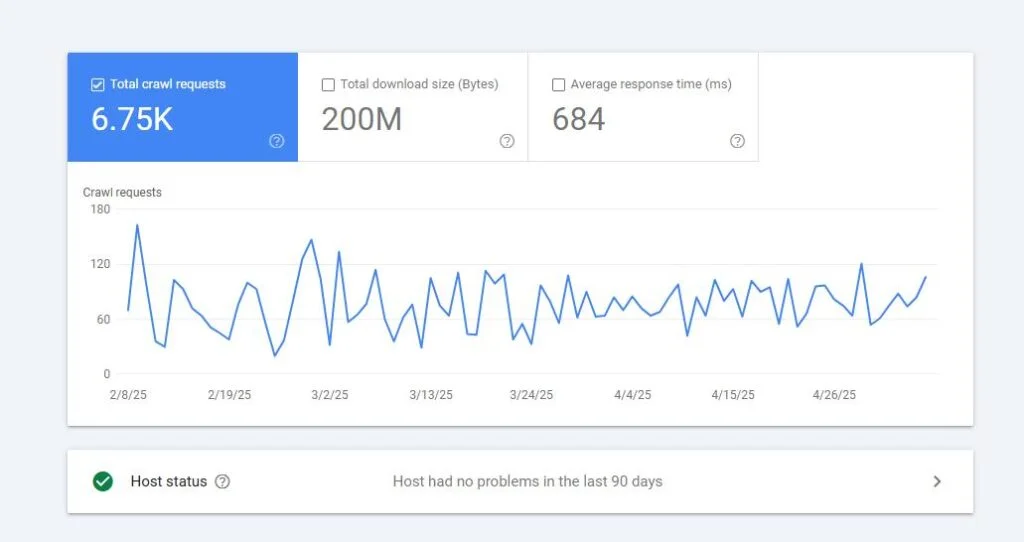
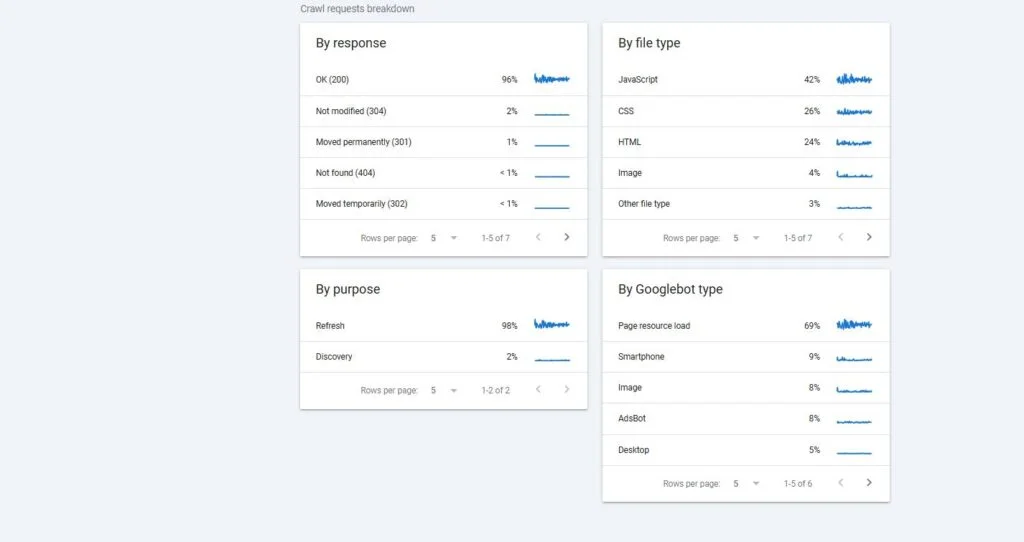
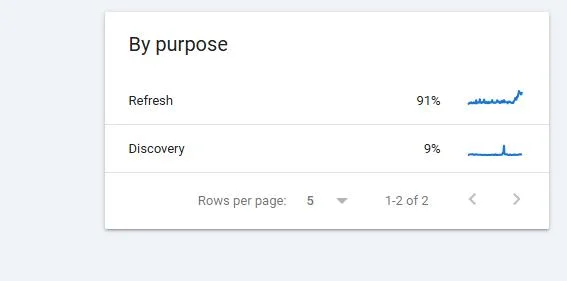
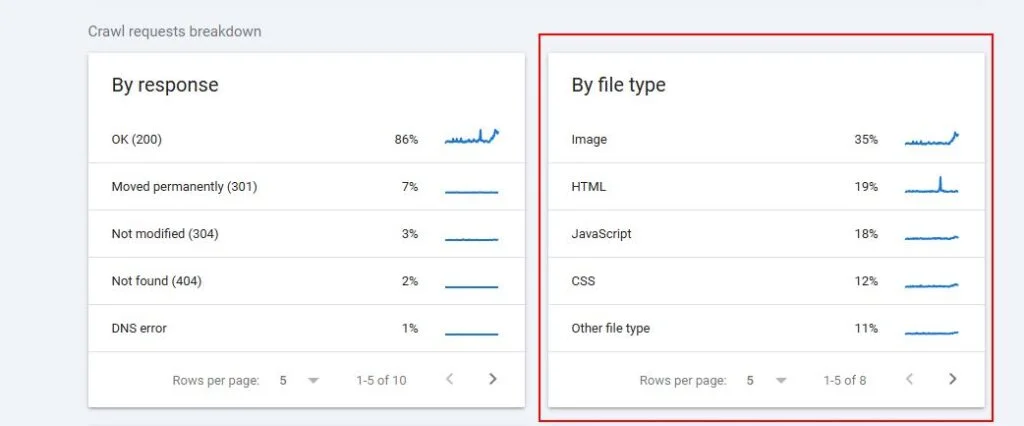
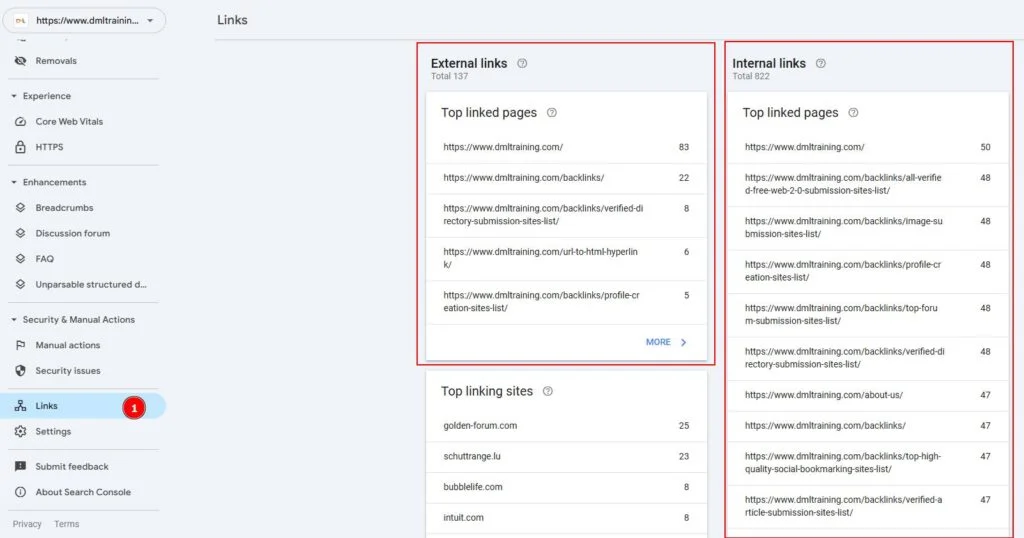
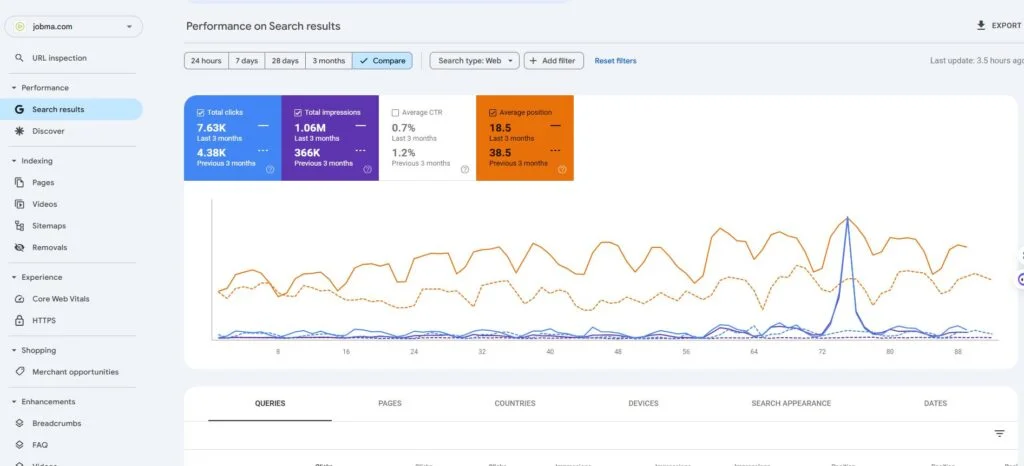
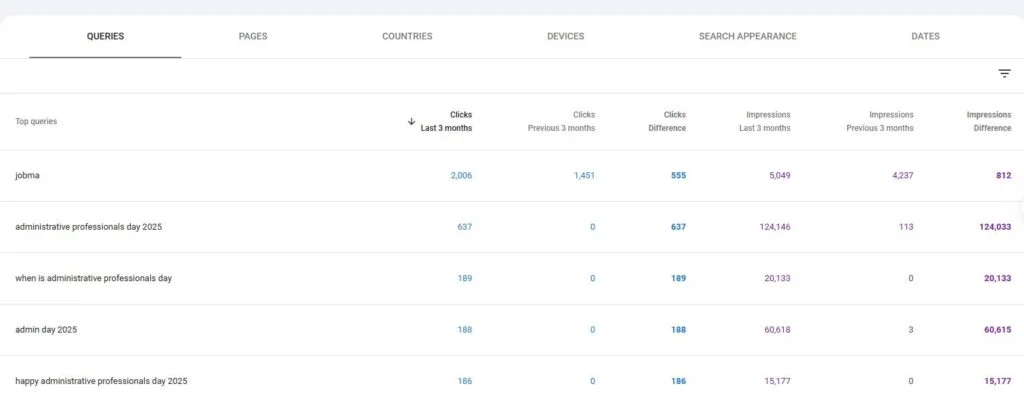
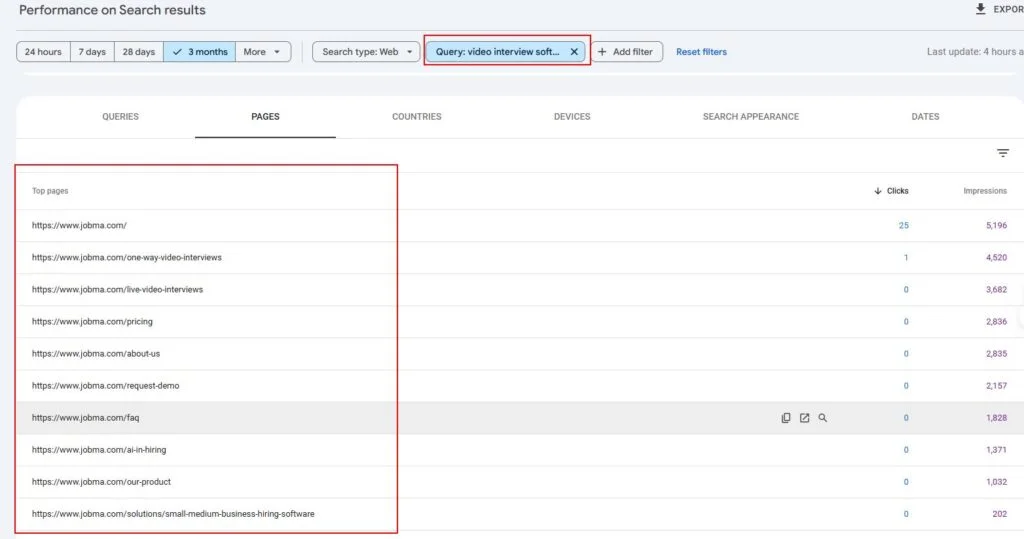
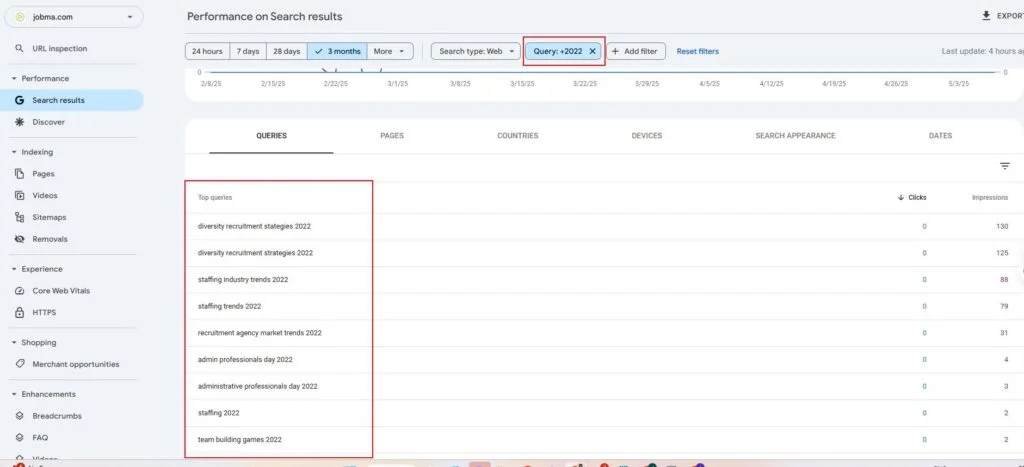
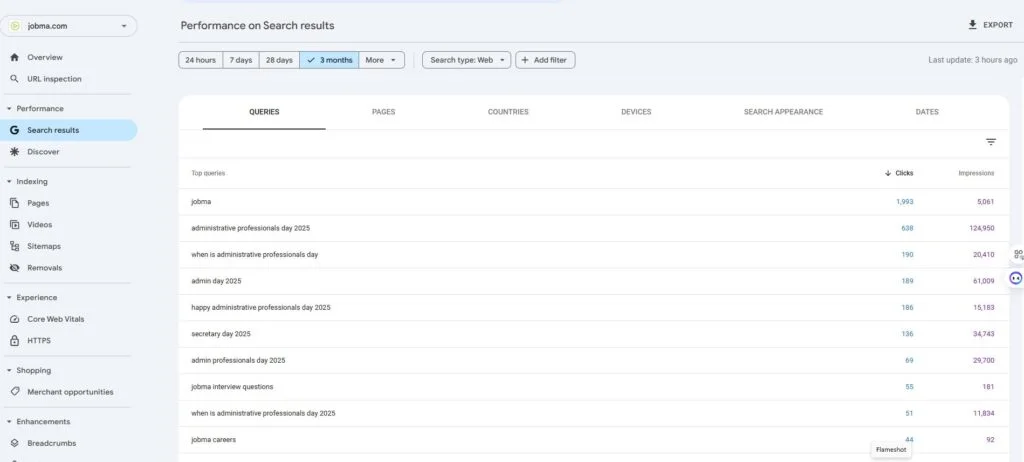
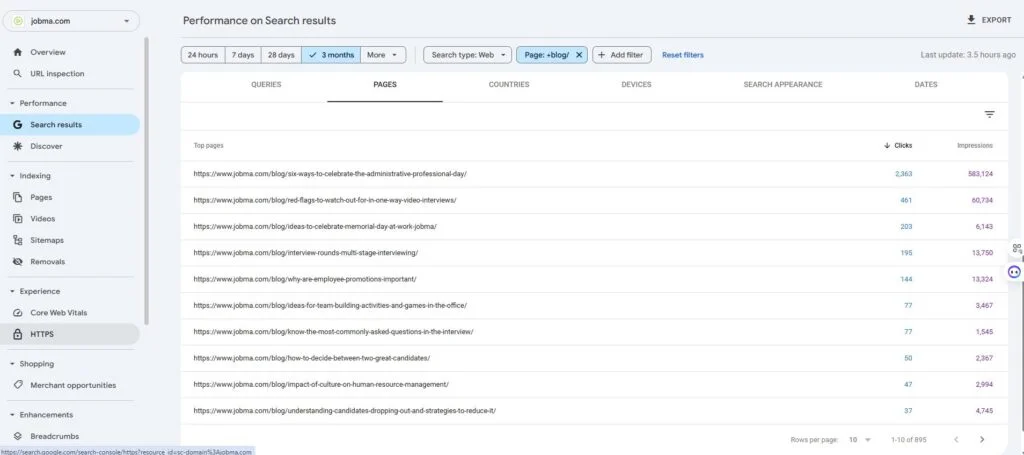
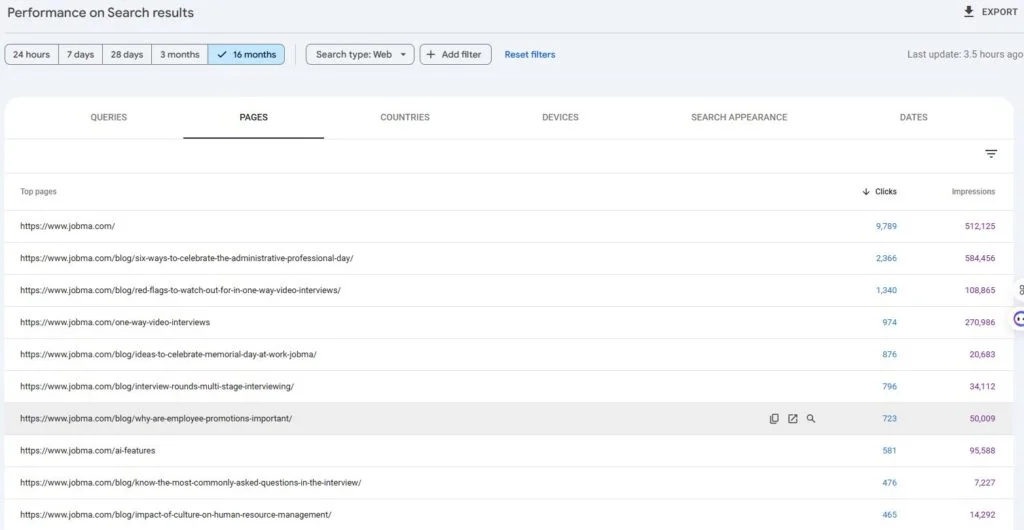
 Format errors in robots.txt
Format errors in robots.txt Issues with blocked internal resources in robots.txt
Issues with blocked internal resources in robots.txt Issues with blocked external resources in robots.txt
Issues with blocked external resources in robots.txt 1. It Dilutes Your Rankings When several of your pages compete for the same keyword, Google doesn’t know which one to rank higher — reducing the potential performance of all pages involved.
1. It Dilutes Your Rankings When several of your pages compete for the same keyword, Google doesn’t know which one to rank higher — reducing the potential performance of all pages involved.